Solutions Automated Guided Vehicles
Improve productivity, reduce product damage, increase efficiency and safety, all with a quick ROI
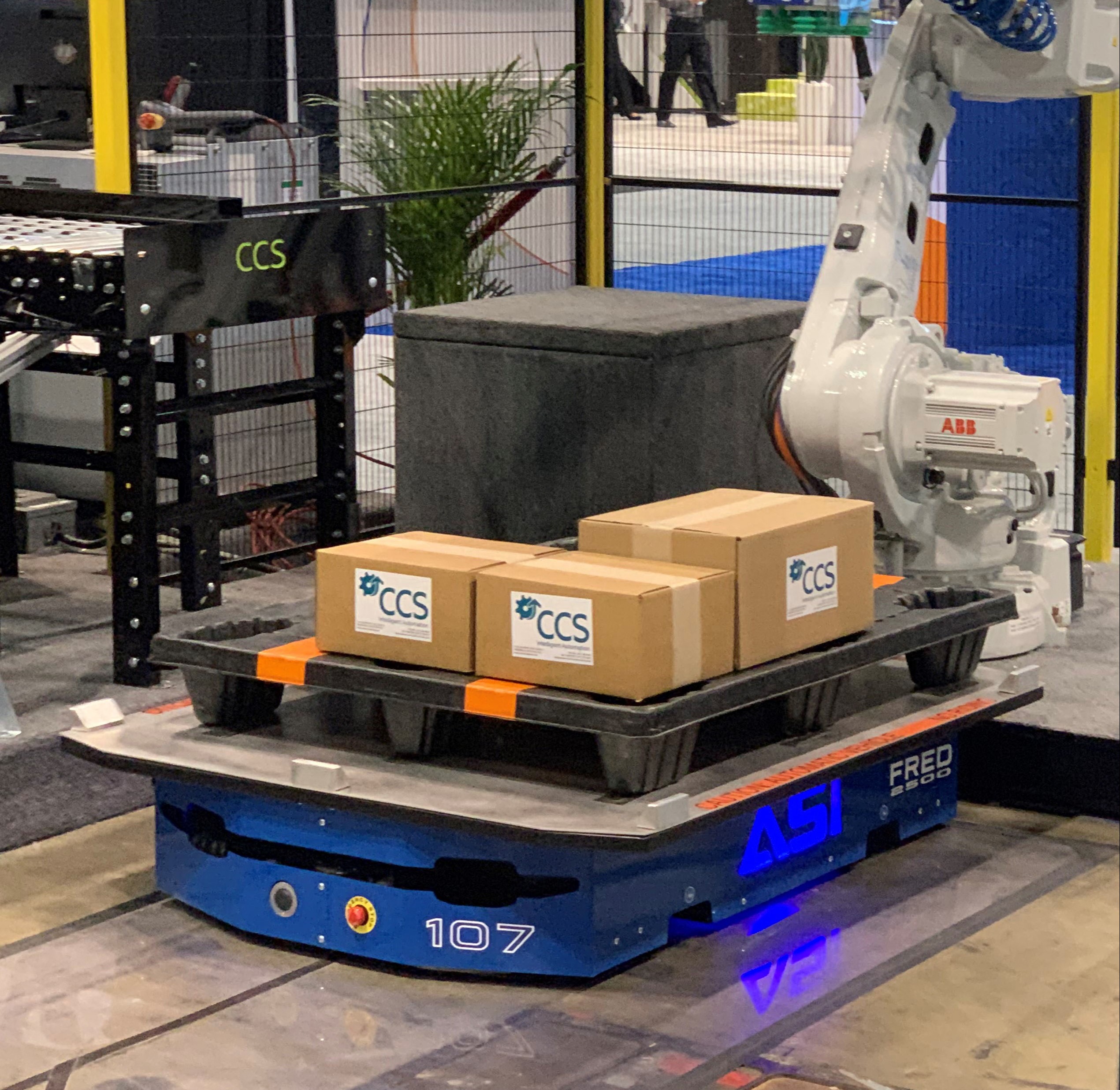
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
An automated guided vehicle or an automatic guided (AGV) robot is a portable robot that follows or uses radio waves, vision cameras, magnets or navigational lasers along marked long lines or wires on the floor. They are used in industrial applications most often for transporting heavy materials, such as a factory or warehouse, to a large industrial building. During the late 20th century, application of the automatic guided vehicle expanded.
PALLETS, PARCELS, PRODUCTS...WE MOVE IT ALL
Automated Guided Vehicle Types

Wired
A slot is cut into the floor of the floor and about 1 inch underneath the surface of the wire. This slot is split in the path to be taken by the AGV. This wire is used for a radio signal transmission. On the base of the AGV near the ground, a sensor is mounted. The sensor detects the radio signal's relative position from the wire. This data is used to control the steering system, so that the AGV follows the cord.

Guide Tape
The AGV is equipped to monitor the ring path with a guide sensor. An important benefit of tape over wired guidance is that if the path needs to change, it can be easily removed and moved. Originally, colored tape is less expensive; however, it does not have the ability to be inserted into high traffic areas where the tape can become dusty. The floor also can be mounted with a flexible magnetic bar, but it is operated in the same way as magnetic band and is therefore still powerless or passive.
Vision Guided
Vision-Guided AGVs can be installed without any changes to the environment or infrastructure. They operate using cameras to record features along the route, allowing the AGV to replay the route using the recorded features to navigate.





